Cell is a fundamental unit of Life Class 9th notes (part 1)
Some important terms
- Numerous living & non-living structure that present in the cytoplasm of cell collectively called Cytoplasmic inclusion.
- During protein synthesis many ribosomes are aggregated due to common messenger RNA and form Polysomes.
- Movement of substance from a region of high concentration to region of low concentration is called Diffusion.
- Osmosis is a special type of diffusion of water that occurs through a semi –permeable membrane. It is of two types:
- When water diffuse into the cell due to its higher concentration outside, it is called Endosmosis.
- When water diffuses out of the cell because of its higher concentration inside the cell, it is called Exosmosis.
- The branch of biology that deals with the various aspects of structure, chemistry, development, genetics & functioning of cells is called cell -biology.
- That membrane which allows certain substances through it called selectively permeable membrane.
- Instrument used to measure the osmotic pressure is called osmometer.
- Shrinkage of protoplast of a cell from its cell wall under the influence of a hypertonic solution is called Plasmolysis.
- DNA + HISTON PROTEIN = CHROMOSOME In human cell 46 chromosomes is present.
- DNA is circular in prokaryotic cell while in eukaryotic cell it is linear.
- Mycoplasma is also called PPLO
- First microscope was built by Zacharias Janssen.
- Pigment Carotene responsible for changing of fruit colour during ripening (from green to yellow or reddish).
- Yellow pigment called Xanthophylls.
- Chloroplast is found in Mesophyll cells. It is the site where photosynthesis occurs.
Cell theory
The theory was jointly put forward by Mathias Jacob Schleiden & Theodor Schwann in their paper `Microscopic investigations’ that based on the similarity of structure and growth in animals and plants. This theory state that the bodies of all living organisms are made up of cells and their products so that cells are units of both structure and function of living organisms. Schleiden and Schwann compared their findings and formulated the cell theory in their joint paper in 1839. The theory proposed that cells are the units of both structure and function of organisms. Cell theory is also called cell doctrine.
Fundamental feature of cell theory
- All living organism are composed of cells and their products.
- Each cell is made of a small mass of protoplasm containing a nucleus in it.
- All cells are basically same in chemical & physiological sense.
In coming year the cell theory was to be extended by Karl Nageli. In 1846 he showed that cell arises from the division of pre-existing cells. In 1855 Rudolf Virchow gives a statement that was “omnis cellula e cellula” it means every cell from a cell thus he gave the significance of cell division in reproduction of organism. In 1858 Virchow published his classical text book Cellular Pathology. Later in 1865 Louis Pasteur gave experimental evidence to support Virchow’s extension of cell theory. The modern version of cell theory state that:
- Growth of an organism involves growth & multiplication of its cell.
- Life exists in the cells because all activity of life is performed by cell.
- A cell can survive independently but its organelle cannot survive independently.
- New cells are arising from pre-existing cells.
- Genetic information stored & express in cell.
- Activities of an organism are the sum total of activities and interactions of its constituent cell.
Objection
- Virus are acellular and do not have cell machinery. Even then they considered as organism.
- Bacteria and cynobacteria do not have nucleus and membrane bound organelle.
- RBCs and Sieve tube cell continue to live without nucleus.
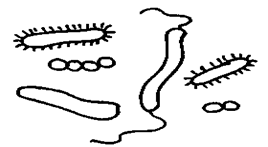
Shapes of cell
The cells vary in their shapes. They may be disc like, polygonal, columnar, cuboids, amoeboid, thread like or irregular. The shape of cell is related to its position and function. Some of shapes are:


Cell size
- There is a wide variation in size & shape of cell. The smallest cell is of Mycoplasma (pleuro pneumonia like organism). They have size of 0.1—0.5µm. longest cell of human body are the nerve cells which may reach a length of 90cm.
- Eggs are large cells because they store food for development of the embryo. Egg of ostrich is large egg cell.
Structural organisation of cell
The protoplasm of cell generally divided into three parts:
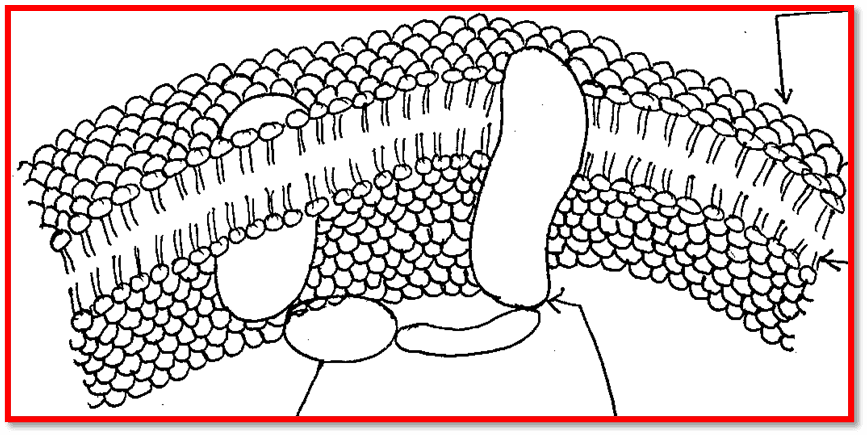
Plasma membrane
it is selectively permeable covering of the cytoplasm that forms the innermost component of cell envelope. It is made up of phospholipids bilayer with protein of various types. Plasma membrane holds the liquid of cell & separates it’s from surroundings, serve as selective permeable membrane. It allows useful substance inwards and harmful substances outwards. It perform following functions:
- It provides & maintains shapes of cells.
- It provides mechanical support & protection.
- It allows only useful substances to enter into the cells.
- It provides specificity to cells.
Cell wall
In case of plant cells outer to plasma membrane is present a non-living and rigid cell wall made up of cellulose. It allows substances freely to enter or to leave it. It performs following function:
- It maintain the shape of cell
- It provide rigidity as well as elasticity to cell
Cytoplasm
the bulk of the cell is made of a dense, viscous, colloidal mass called cytoplasm. It presents b/w plasma membrane and nuclear membrane. It is the site where all metabolic activity takes place. Cytoplasm of unicellular organisms is differentiated into outer ectoplasm and inner endoplasm. There are various cell organelles.
Endoplasmic reticulum
A inter connected network of membrane – lined channels called endoplasmic reticulum. The name endoplasmic reticulum was coined by Porter in 1953 in liver cell.
It is visible only under electron microscope.
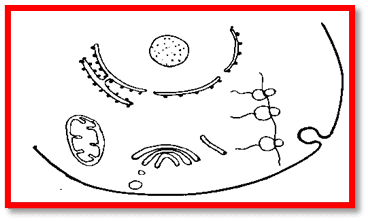
It is connected with the plasma membrane, Golgi body & nuclear membrane. It helps in the formation of other organelles. It is of two types:
- RER–it is rough in appearance because ribosome present on its surface. Functions are following: endoplasmic reticulum provides ultra structure skeletal framework to cell and give mechanical support, it is the site for protein synthesis& it forms nuclear envelope after each nuclear division.
- SER–it is found mostly in the outer part of cytoplasm. It is smooth because absence of ribosome on its surface. Functions are following: synthesis of lipid, sterol metabolism, it concerned with glycogenolysis & detoxification.
Golgi body
Golgi body is also called Golgi apparatus. It was coined by Camillo Golgi& S.R. Golgi. The Golgi body occurs in all cells except the prokaryotic cells of certain fungi, bryophytes & pteridophytes and also RBCs of animal cells. Their number varies from cell to cell. They are more than 25000in algal rhizoid. In animal cells there usually occur a single Golgi apparatus, its no. may vary from cell to cell. It is divided basically in three parts: cisternae, tubules & vesicles. It concerned with the following function: secretions, membrane flow, formation of lysosomes and formation of vitelline membrane of primary oocytes. In plants it forms cell plate.
Mitochondria
These are popularly known as Powerhouse of cell. Mitochondria are granular cytoplasmic organelles of all aerobic cells of higher animals & plants and also of certain m/o including algae, protozoa and fungi.
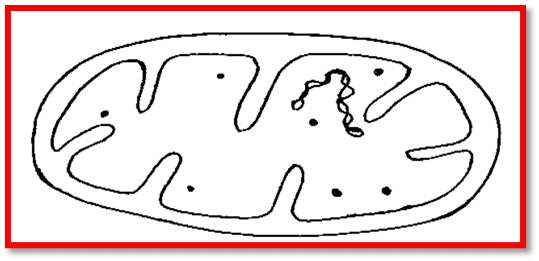
- They also contain a specific DNA for cytoplasmic inheritance.
- Mitochondria were first discovered by the Kolliker in 1850 in striated muscles. The number of mitochondria in a cell depends on the type and functional state of cell. Liver cell of rat contain 500 to 1600 mitochondria. Mitochondria area double membranous structure that has various enzymes because it is the site for various metabolic reactions.
Function: it is the site where ATP is formed due that it is called powerhouse of cell
Ribosome
These are the granular structure that is seen under electron microscope. They occur either freely in the matrix of mitochondria, chloroplast & cytoplasm or remain attached with the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum &nucleus. When they attached to the endoplasmic reticulum then they called RER. In 1952, G.E. Palade describes the ribosome. On the basis of sedimentation coefficient, it is of two types: 70S & 80S. Ribosome helps in the protein synthesis so called protein factory.